Testing that Reaches the World
Telcordia / Belcore GR-63
Structures and equipment installed in Data Centers located in active seismic regions must be designed to protect the operating equipment in the event of an earthquake. There are two standards by which enclosures are deemed seismically qualified: Telcordia Technologies GR-63-CORE Network Equipment Building Systems (NEBS) requirements and the International Building Code (IBC). These standards are used to achieve the seismic certification to comply with specific code requirements.
Clark’s Seismic and Vibration Labs provide the full Telcordia / BELCORE GR-63 CORE suite of seismic, transportation vibration, office vibration, salt spray, EMC and more. As required by Telcordia, Clark maintains an ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation with A2LA.
Clark’s in-depth safety programs facilitate the seismic and vibration testing of large Lithium-Ion battery racks and battery back-up systems. Our team is well trained to handle the additional spill and fire risks associated with hazardous material testing.
Clark’s primary tri-axial seismic shake table is comprised of a 15’ x 15’ mounting surface (which can be extended up to 26’) operating on an independent tri-axial hydraulic system. Using this system, our engineers can perform seismic testing on large packages up to 25,000 lbs. The table has three independent servo hydraulic actuators with 38,000 lbs. force each and 10” of peak-to-peak displacement.
During a typical GR-63 seismic test, the test equipment is loaded to its capacity and mounted to Clark’s Tri-axial seismic shaker table. Clark lab technicians install instrumentation including accelerometers, strain bolts, and displacement sensors to the equipment under test. Once complete, the shaker table simulates an earthquake, shaking in three directions (one direction at a time) at varying levels of intensity, equivalent to an earthquake in the required seismic zone — Zone 0 is the least intense; Zone 4 is the most intense. In order to pass the test and achieve the seismic rating, the equipment must not sway more than 3 inches in any direction and all components must remain operable before and after the test.
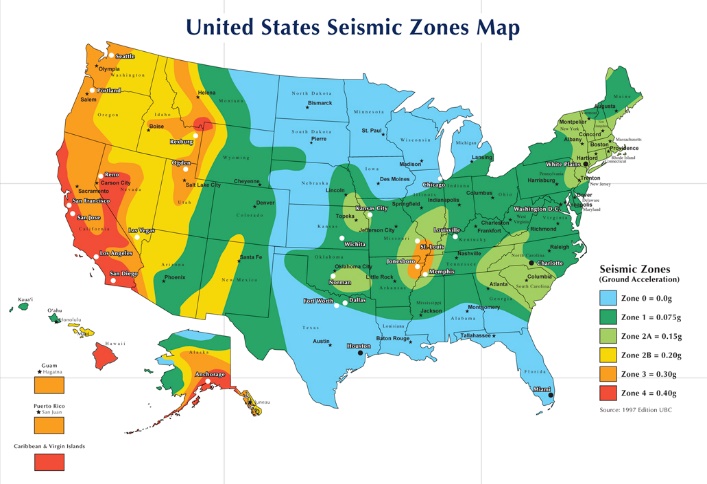
Seismic test levels are often specified in terms of the earthquake risk zones. As shown on the seismic map, zones range from 0 to 4, with Zone 4 indicating the most severe and Zone 0 indicating the least.
